- Home
- >
News
XRD technology is widely used in the fields of crystallography, physics and metallurgy, including qualitative and quantitative, crystal structure, mechanical analysis, etc. This paper mainly lists its application in polymer research.
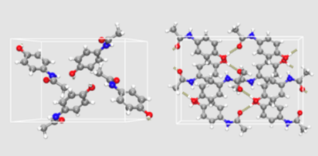
In drug research and development, crystal research runs through all stages from the screening of lead compounds to the final drug marketing.
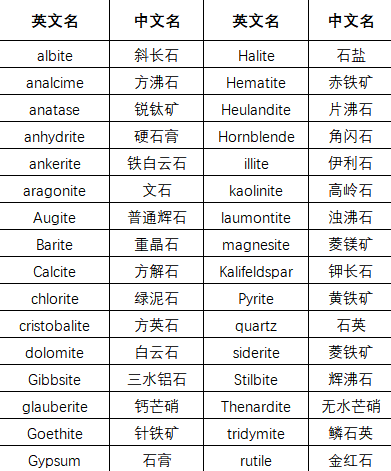
Petrological studies often require the identification of mineral compositions in rocks, especially those that are less abundant. Therefore, the qualitative analysis of minerals is the most important application of X-ray diffraction in the study of mineral petrology.
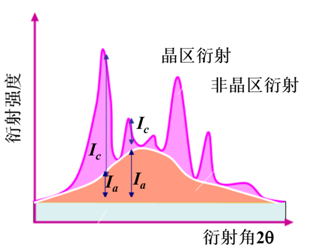
Polymers are commonly synthesized as fibers, sheets, and other solid forms. Its properties are greatly affected by its structural parameters such as crystallinity, crystal structure and orientation, and can be studied using XRD
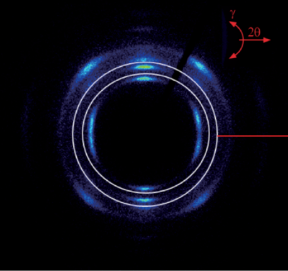
X-ray diffraction is divided into two kinds of single crystal diffraction and powder diffraction, single crystal is mainly used for the determination of molecular weight and crystal structure, powder is mainly used for the identification and purity of crystalline substances.
With the development of XRD detection technology, instrument miniaturization, low energy consumption, simple use, intelligent detection is becoming more and more popular, and has become the trend of instrument update.
The polycrystalline phenomenon of drugs refers to the formation of different crystal states of a compound molecule in the solid state due to the different crystal arrangement and filling methods.
Asbestos, also known as "asbestos", refers to silicate mineral products with high tensile strength, high flexibility, resistance to chemical and thermal erosion, electrical insulation and spinnability. The three most common types are chrysotile, iron and cyanite.
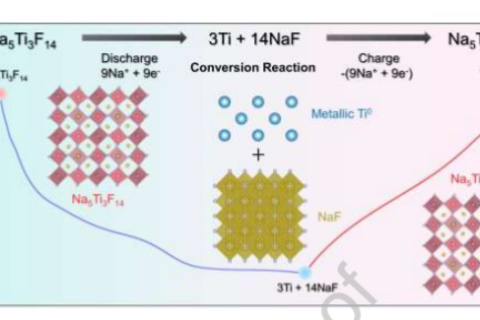
Sungkyunkwan University in South Korea has demonstrated that nano-Na5Ti3F14 / carbon nanocomposites have excellent electrochemical properties as the negative electrode of sodium-ion batteries.
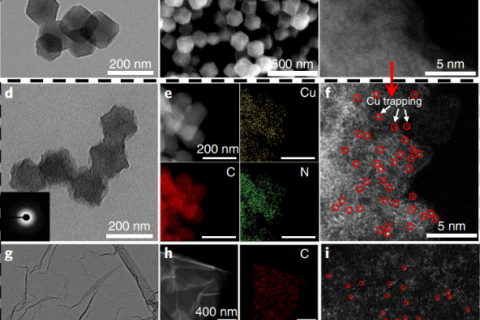
Characterization methods of copper monatomic catalysts are often used to determine their structure and properties, and the following are several common characterization methods.
Cement is a common building supplies, generally divided into ordinary Portland cement, Portland cement mixed materials and special cement, the use of Portland cement is more.
Recently, Applied Clay Science reported "High-pressure Raman scattering and X-ray diffraction study of kaolinite, Al2Si2O5(OH)4."