- Home
- >
News
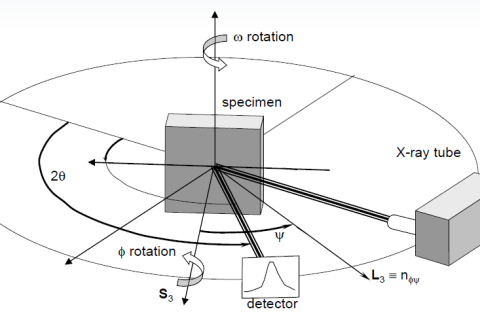
Residual stress has a great impact on the dimensional stability, stress corrosion resistance, fatigue strength, phase change and other properties of materials and components. Its measurement has been widely concerned by academia and industry.
XRD, is short for X-ray diffraction, as a material person, no matter what material is done, XRD is the most commonly used, the most basic means of characterization.
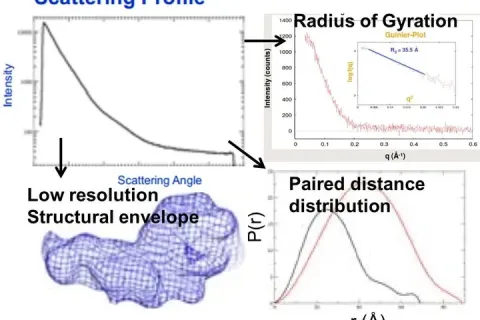
When a beam of extremely thin X-rays passes through a material with an uneven electron density of nanometer size, the X-rays will spread out in a small angular region near the direction of the original beam, this phenomenon is called small-angle X-ray scattering.
Small Angle X-ray diffraction (SAXD) is mainly used to determine the spacing of very large crystal faces or the structure of thin films.
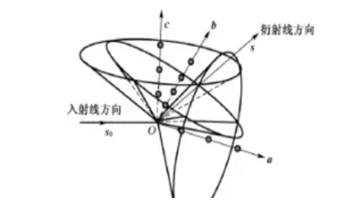
The use of X-rays to study the structure of crystals mainly through the X-ray diffraction phenomenon in the crystal.
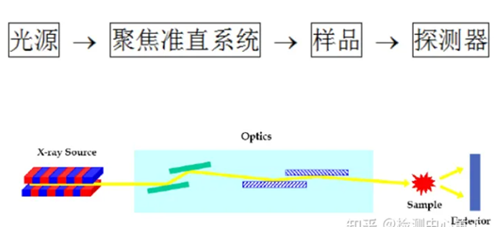
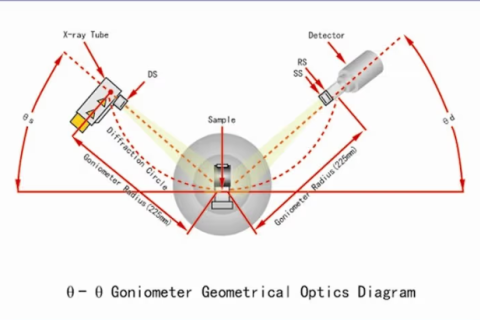
X-ray diffraction technique is an analytical method used to study the structure of a substance. It determines the structure of a crystal by measuring the Angle of X-ray diffraction in the crystal.
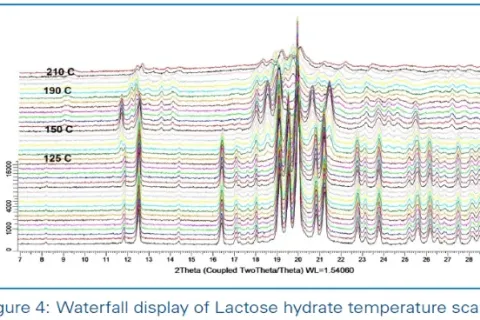
In-situ XRD, also known as In situ X-ray Diffraction, is a technique for making X-ray diffraction measurements during a structure or phase transition. This technology can monitor the dynamic change of the structure of the material under external force in real time.
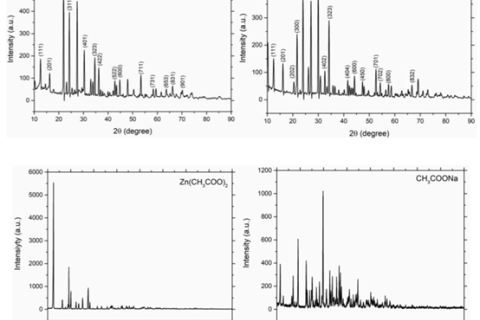
In materials science research, X-ray diffraction (XRD) is an important experimental method. Through XRD data, we can obtain information such as grain size, lattice distortion and dislocation density.
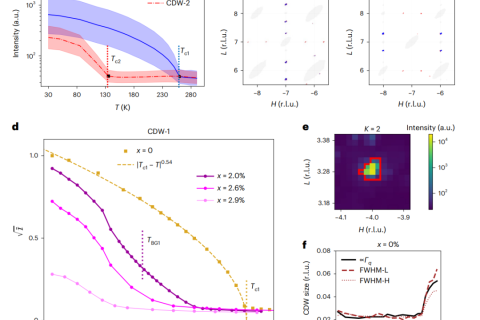
The Bragg glass phase is a near-perfect crystalline phase with glassy characteristics that is expected to occur in vortex lattices and charge density wave systems in the presence of disorder.
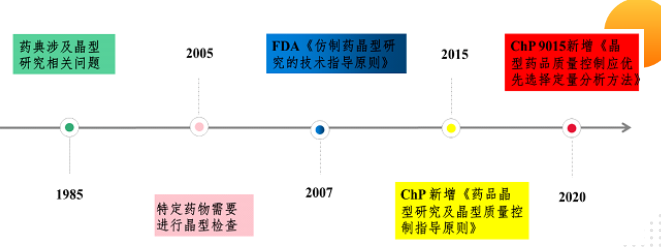
X-ray diffraction technique is widely used in drug analysis. X-ray diffraction technique is an analytical method used to study the structure of a substance. This technique has many applications in drug analysis.
The stronger the light, the brighter? But this is not always the case. When the intensity of the X-ray beam begins to exceed a certain critical value, the diffraction image unexpectedly weakens.