X-ray absorption fine structure XAFS
XAFS Spectrometer achieves synchrotron-level data quality with >4M photons/s/eV flux, <0.1% stability, and a 1% detection limit. It empowers research across energy, catalysis, and materials science.
- Tongda
- Liaoning, China
- 1—2 months
- 100 units per year
- Information
| Parameter | Description | |
| Comprehensive Performance | Energy Range | 4.5-25keV |
| Spectrum Acquisition Mode | Transmission Mode | |
| Photon Flux at the Sample | >4×10⁶ photons/(s·eV) | |
| Energy Resolution | XANES:0.5-1.5eV EXAFS:1.5-10eV | |
| X-ray Path | Helium purge path to minimize air absorption | |
| Repeatability | Reproducible energy drift < 50 meV | |
| Structure | The dual Rowland circle configuration eliminates the need for light source switching during XAFS measurements. Utilizing a single dedicated XAFS X-ray source to generate a dual X-ray beam, the system provides two energetically monochromatic X-rays through dual Rowland circles and dual monochromators. This enables simultaneous characterization of two metal elements within the same sample, permitting parallel analysis of the local atomic structures of both metallic elements. | |
| X-ray Source | Power | 2.0 kW; High voltage: 10-40 kV; Current: 1-50 mA |
| Target | Standard with W/Mo targets; other target materials available as options | |
| Monochromator | Type | Spherical analyzer crystal with 500 mm radius of curvature and 102 mm size |
| Detector | Type | Large-area SDD with a 150 mm² active area |
| Additional Configurations | Sample Changer | 18-position sample changer for continuous automated testing of multiple samples |
| In Situ Sample Cell | In situ cells for various conditions: electrocatalysis, temperature-varying, multiphysics fields, and mechanical testing | |
| Analyzer Crystal | Specialized crystal monochromator for specific-element analysis |
Core Advantages:
Highest Photon Flux: Our product delivers a photon flux exceeding 4,000,000 photons/s/eV, offering spectrum acquisition efficiency several times higher than comparable systems. This enables data quality on par with synchrotron radiation sources.
Exceptional Stability: The instrument features excellent monochromatic light intensity stability, with variations of less than 0.1%. Reproducible energy drift during repeated acquisitions is maintained below 50 meV.
1% Detection Limit: The combination of high flux, superior optical path optimization, and exceptional source stability ensures the acquisition of high-quality EXAFS data, even for elemental concentrations as low as 1%.
Instrument Principle:
The X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (XAFS) spectrometer is a powerful tool for investigating the local atomic and electronic structure of materials. It is widely applied across various prominent fields, including catalysis, energy research, and nanoscience.
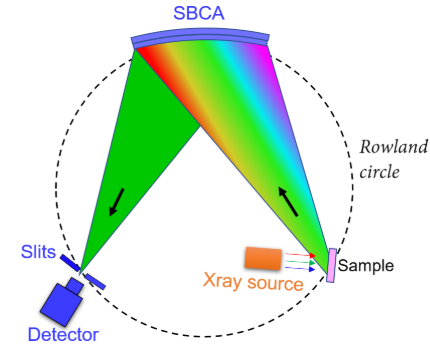
Laboratory Monochromator XES Testing Geometry
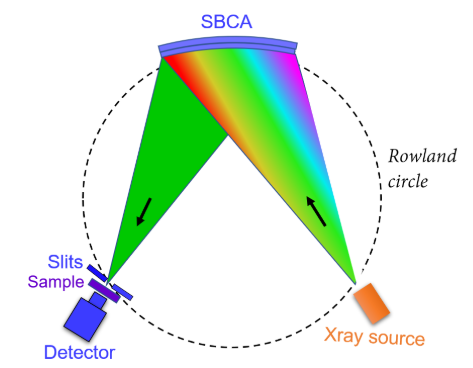
Laboratory Monochromator XAFS Testing Geometry
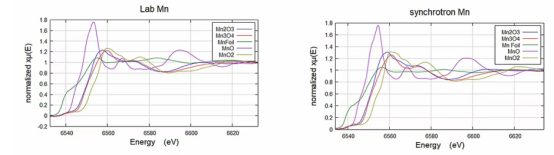
Manganese (Mn) Data and Mn K-edge XAFS Data: Consistent with Synchrotron Radiation Source Quality

Kβ Emission Spectrum Data of Iron (Fe) Sample: Core-to-Core XES and Valence-to-Core XES
Test Data
Foil EXAFS Data

Applications
This XAFS spectrometer finds wide-ranging applications, empowering clients to make breakthroughs across multiple fields:
New Energy: Used in the study of fuel cells, hydrogen storage materials, lithium-ion batteries, etc. It can analyze the dynamic changes in the valence state and coordination environment of central atoms during catalytic processes.
Industrial Catalysis: Applicable to research areas like nanoparticle catalysis and single-atom catalysis. It can characterize the morphology of catalysts on supports and their interactions with the support material.
Materials Science: Employed for the characterization of various materials, the study of complex systems and disordered structures, as well as investigating the properties of surface and interface materials.
Environmental Science: Can be utilized to analyze heavy metal contamination in samples such as soil and water, determining the valence state and concentration of elements.
Biomacromolecules: Can be used to study the local atomic structure around metal centers in metallobiomolecules .