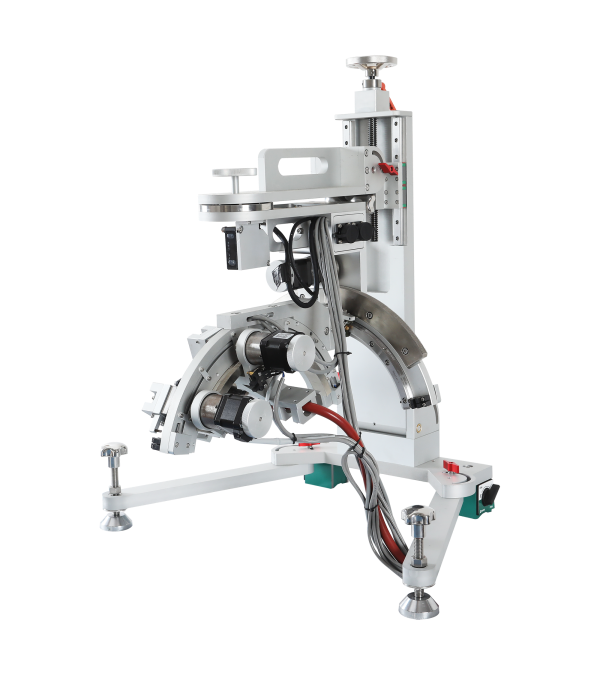
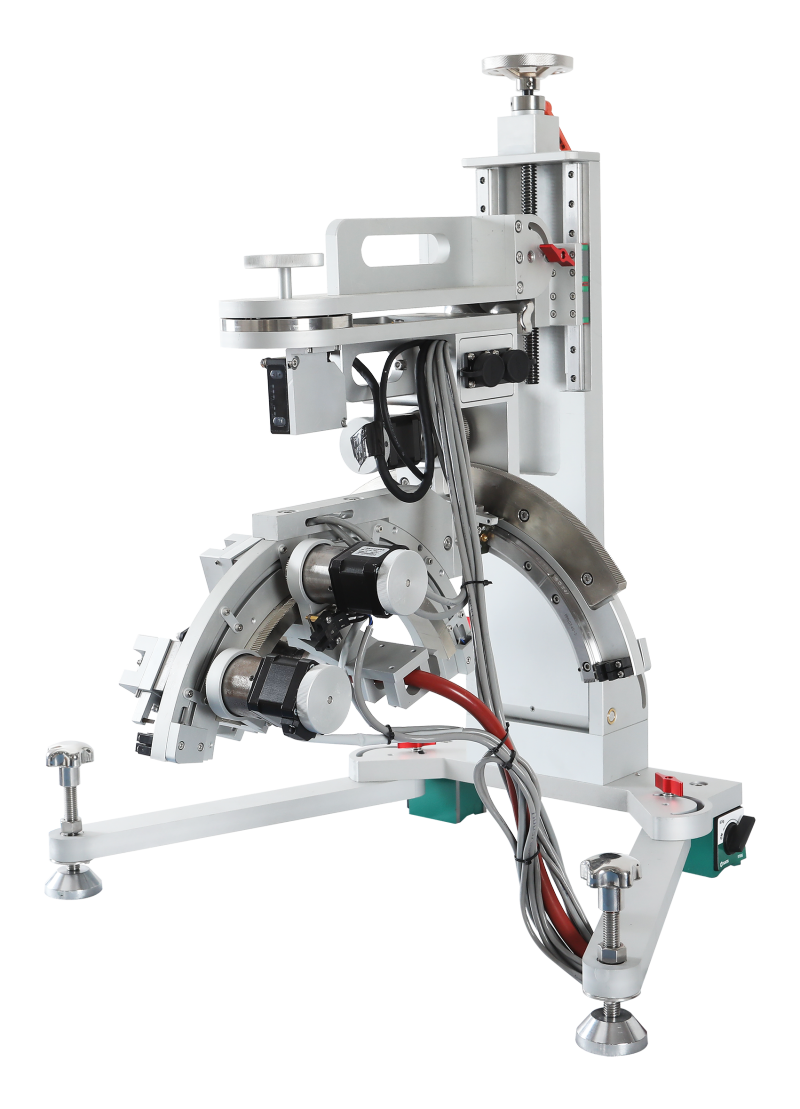
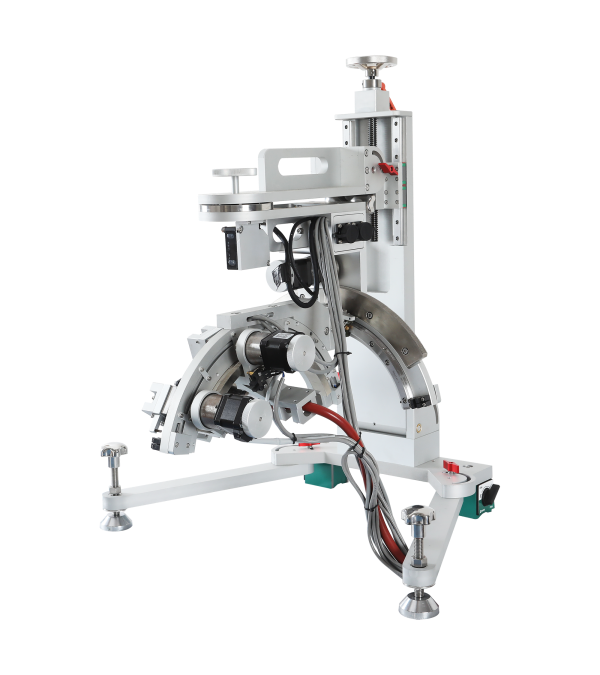
Multi-functional Residual Stress Analyzer
PLC control system;Modular design, easy operation, and more stable equipment performance
Lightweight design: Lightweight, suitable for rapid on-site measurement;
High-precision measurement: High-precision full-closed-loop vector drive servo system control;
Simple operation: Integrated Windows system or automation functions, supports one-click testing and real-time result display;
Multi-functional compatibility: Measuring carbon steel, alloy steel, titanium alloy and other metals, glass, nickel-based materials and various composite materials;
Speed optimization: Multi-channel silicon microstrip line array detector can provide noise-free performance, high-intensity measurement and rapid data acquisition.
- Tongda
- Liaoning, China
- 1—2 months
- 100 units per year
- Information
Residual Stress Generation:
During processes such as rolling, forging, extrusion, drawing, bending, and stamping, the material surface layer undergoes significant deformation (plastic deformation), while the core experiences minimal deformation (elastic deformation).
Machining/grinding: Cutting tools or grinding wheels exert intense compression, shear, and friction on the workpiece surface, leading to severe plastic deformation and even microstructural changes in the surface layer.
Shot peening/sandblasting/roller pressing: High-speed projectile impacts or roller compression cause local plastic flow (such as surface layer extension) on the material surface, all of which generate residual stress.
Multifunctional Testing:
Rapid analysis of residual stress in materials such as carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel (austenitic, duplex stainless steel, martensitic steel), nickel-based materials (N08810, N08120, N04400, N06600, N06617, etc.), titanium alloys (pure titanium, α-type titanium alloys, α+β-type titanium alloys), aluminum, alumina, copper, copper oxide, zirconium, zirconium alloys, silicon nitride, silicon carbide, etc., in forms including plates, pipes, field welds, and heat-affected zones.
Compliant with international and national standards for the sin²ψ method: ASTM E915-21, EN15305-2008, GB/T 7704-2017, JJF1083-2023, and JB/T9394-2011.
Laser auto-focusing and distance measurement, enabling non-destructive and rapid testing.
Three-axis multi-directional testing capability, with flexible rotation of the measurement unit for multi-angle analysis.
Quick analysis of residual stresses in sheet materials, pipe materials, on-site welds, and heat-affected zones of carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel (austenitic, duplex stainless steel, martensitic steel), nickel-based materials (N08810, N08120, N04400, N06600, N06617, etc.) and titanium alloys (pure titanium, a-type titanium alloy, α+β type titanium alloy), aluminum, alumina, copper, copper oxide, zirconium, zirconium alloys, silicon nitride, silicon carbide, etc.
Conforms to international and domestic standards ASTME915-21, EN 15305-2008, GB/T7704-2017, JF1083-2023 and JB/T9394-2011.
Laser focusing distance measurement, non-destructive rapid testing.
3-axis multi-dimensional direction testing, measurement unit with flexible rotation at multiple angles
Multi-functional Residual Stress Analyzer
Residual Stress Analysis
Standard synchronous inclination method. Standard heel test Standard rolling test;
Measurement of Principal Stresses and Shear Stresses.
Residual austenite analysis
Four-Peak Method for Retained Austenite Measurement;
Fully Automated Data Computation.
Diffraction Phase Analysis
Analyze the crystalline structure,chemical composition, and distribution of the substance;
2 theta ranges from 30 degrees to 170 degrees.
Grain Size Analysis
Grain size analysis from the nanoscale to the submicron scale;
Suitable for grains with sizes ≤200nm.